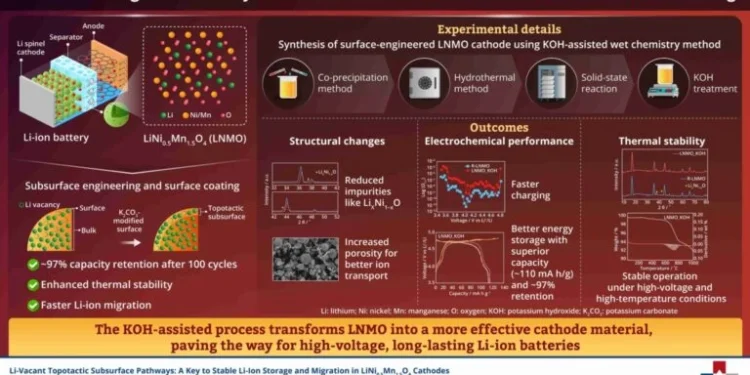
According to Yahoo Finance, a research team from Seoul National University of Science and Technology has unveiled a groundbreaking innovation in lithium-ion battery technology, introducing a new method to enhance the stability, efficiency, and energy density of lithium-ion batteries. The study, led by Professor Dongwook Han, focuses on modifying high-voltage lithium nickel manganese oxide (LNMO) cathodes, highlighting a major advancement in high-energy-density batteries with extended lifespan and faster charging capabilities.
The research team engineered a Li-vacant topotactic subsurface while applying a protective potassium carbonate (K₂CO₃) layer on the LNMO cathode particles. This dual engineering approach addresses one of the major limitations of LNMO cathodes—electrolyte decomposition, which typically reduces battery performance over time. The newly developed LNMO_KOH cathodes achieved 110 mAh per gram discharge capacity, up from 89 mAh per gram, and 97% capacity retention after 100 cycles, surpassing the 91% in conventional LNMO. Their enhanced thermal stability ensures safer and more reliable batteries for electric vehicles and energy storage.
Lithium-ion batteries are the backbone of electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems, but achieving high energy density with long-term stability remains a major challenge. LNMO cathodes are recognized for their thermal stability and cost-effectiveness, but their widespread use has been hindered by side reactions that degrade battery performance. The scalability of this technique offers a cost-effective and high-performance alternative to existing lithium-ion battery technology, paving the way for more efficient and durable energy storage solutions.
Read our latest news on batteriesdaily.