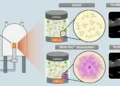
According to APAC News Networks, researchers at the National Institute of Technology (NIT), Rourkela, have announced the development of a magnesium-based cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. This innovation offers a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to cobalt, addressing key challenges in battery manufacturing. The magnesium-based cathode promises enhanced performance, reduced environmental impact, and a significant reduction in the reliance on cobalt, a critical but problematic material in conventional batteries.
Cobalt, commonly used in lithium-ion battery cathodes, poses several issues due to its high cost and limited availability. According to Partha Saha, Associate Professor at NIT Rourkela’s Ceramic Engineering Department, the growing demand for EVs and batteries is expected to exceed cobalt supply by 2050, underscoring the urgent need for alternative materials. Magnesium emerges as a viable solution due to its abundance, particularly in regions such as Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, and Karnataka, and its environmentally friendly profile compared to cobalt. The newly developed magnesium-based cathode demonstrated improved durability, retaining 74.3% of its original capacity after 100 charge-discharge cycles—a notable improvement over traditional cobalt-based cathodes, which frequently experience rapid capacity loss. The research also resolved issues related to cationic disorder in nickel sites, which typically lead to capacity and voltage degradation in conventional batteries.
The magnesium-based cathode represents a transformative step toward producing affordable, high-performance batteries for India’s EV market. The research has far-reaching implications for reducing battery production costs, improving EV adoption rates, and strengthening India’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions. The team at NIT Rourkela continues to work on scaling this breakthrough for commercial applications, marking a significant milestone in battery technology and sustainability.
Read our latest news on batteriesdaily.